Internal Financial Controls Audit (IFC Audit)
Primary objective of IFC Audit is to identify opportunities for improvement and to draw up recommendations and good practices for organizations that can be used as a benchmark to develop or strengthen their internal control systems and enhance the reliability of their financial statements.
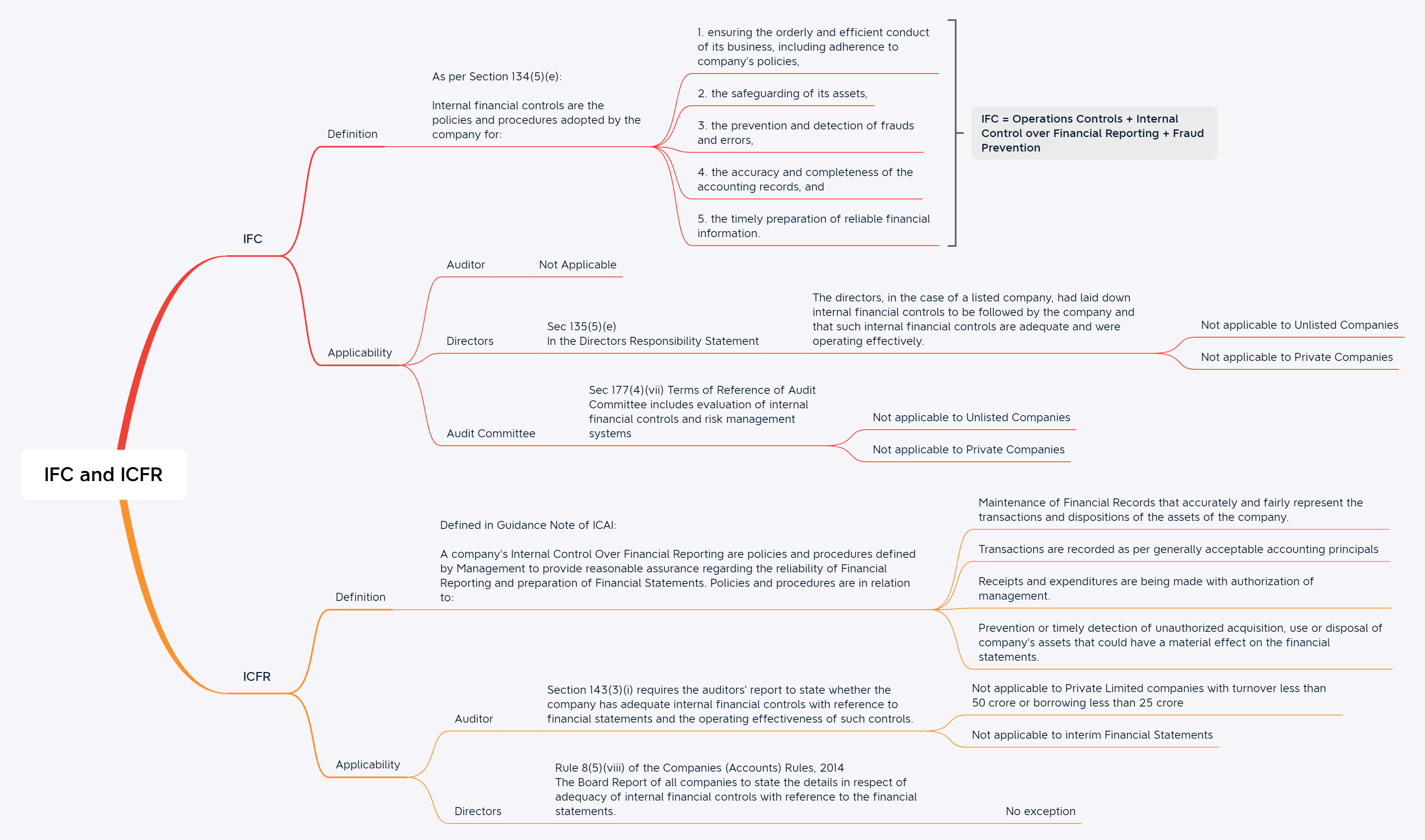
“Internal Control System” means all the policies and procedures (internal controls) adopted by the management of an entity to assist in achieving management’s objective of:
- Ensuring the orderly and efficient conduct of its business, including adherence to management policies,
- Safeguarding of assets,
- Prevention and detection of fraud and error,
- Accuracy and completeness of the accounting records, and
Timely preparation of reliable financial information
Internal control helps entities achieve objectives of the organisation and sustain and improve performance. A benchmark system of internal control, based on suitable criteria, is essential to enable the management to assess the adequacy and compliance of the system of internal control.
Internal Financial Controls Audit involves:
- Studying the “as is” process and providing recommendations with regards to the “to be process” considering the best practices and risk prevention.
- Assessing the adequacy and effectiveness of the existing internal controls designed for each process.
- Reporting on the adequacy and effectiveness of the internal controls.
IFC Audit = ICFR Audit + Operational control Reporting + Fraud prevention Reporting.
Benefits of Internal Financial Controls Audit
As the Management of the company, you will want to have regular feedback on the risk management and efficiency of mitigating the risk of control failures in your organization.
IFC audit services provide a robust mechanism to structure and extend the risk management beyond the financials and extends to the operations that eventually impact the finances of the company.
Internal Controls Over Financial Reporting (ICFR Audit)
Internal financial controls system includes policies and procedures for ensuring the efficiency and effectiveness of business and ensuring the accuracy of accounting records.
Internal Control Over Financial Reporting Audit is designed to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external purposes in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles”. A Company’s internal financial control over financial reporting includes those policies and procedures that:
- Pertain to the maintenance of the records that, in reasonable detail, accurately and fairly reflect the transactions and dispositions of the assets of the company.
- Provide reasonable assurance that transactions are recorded as necessary to permit preparation of financial statements in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles and that receipts and expenditures of the company are being made only in accordance with authorizations of management and the director of the company.
- Provide reasonable assurance regarding the prevention or timely detection of unauthorized acquisition, use or disposition of the company’s assets that could have a material effect on the financial statement.
Internal Controls Over Financial Reporting involves:
- Studying the “as is” process and providing recommendations with regards to the “to be processed” considering the best practices and risk prevention.
- Assessing the adequacy and effectiveness of the existing internal financial controls over financial reporting.
- Reporting on the adequacy and effectiveness of the internal financial controls over financial reporting.
ICFR Audit = Maintenance of financial records (details & Accuracy) + Authorization of Transactions + Safeguarding of assets of the Company
Benefits of ICFR Audit
Internal Control over Financial Reporting provides a robust mechanism to ensure the Design and implementation of the controls are adequate to the size and structure of the organization. It further gives a reasonable assurance on the operative effectiveness of the Internal Financial Controls over financial reporting.
Performance Measurement
The ICFR Audit and IFC Audit is carried out based on an extensive Risk Control Matrix (RCM) covering the organization’s process. The Controls are designed by the expert team based on the understanding of the business process if not already designed. Each year the RCM is reviewed and revised to meet the organization’s ever-changing needs and variations in the process.
The RCM controls are tracked and concluded based on Effective, Ineffective and Design gaps in controls.
Each control is discussed with the process owner and key control deficiencies are communicated and discussed with the Management.
Value Additions from the process involve:
- Helps in business process re-designing to plug revenue leakages & cost containment opportunities.
- Helps in rationalizing the number of controls across organizations – moving to smart and automated controls.
- Helps in standardizing policies and procedures for multi-location/ multi-business companies
- Fosters a control-conscious work culture for people behind controls.
- Provides assurance to the Management, improves business performance, also serves as a blueprint of optimal procedures while thinking about ERP.